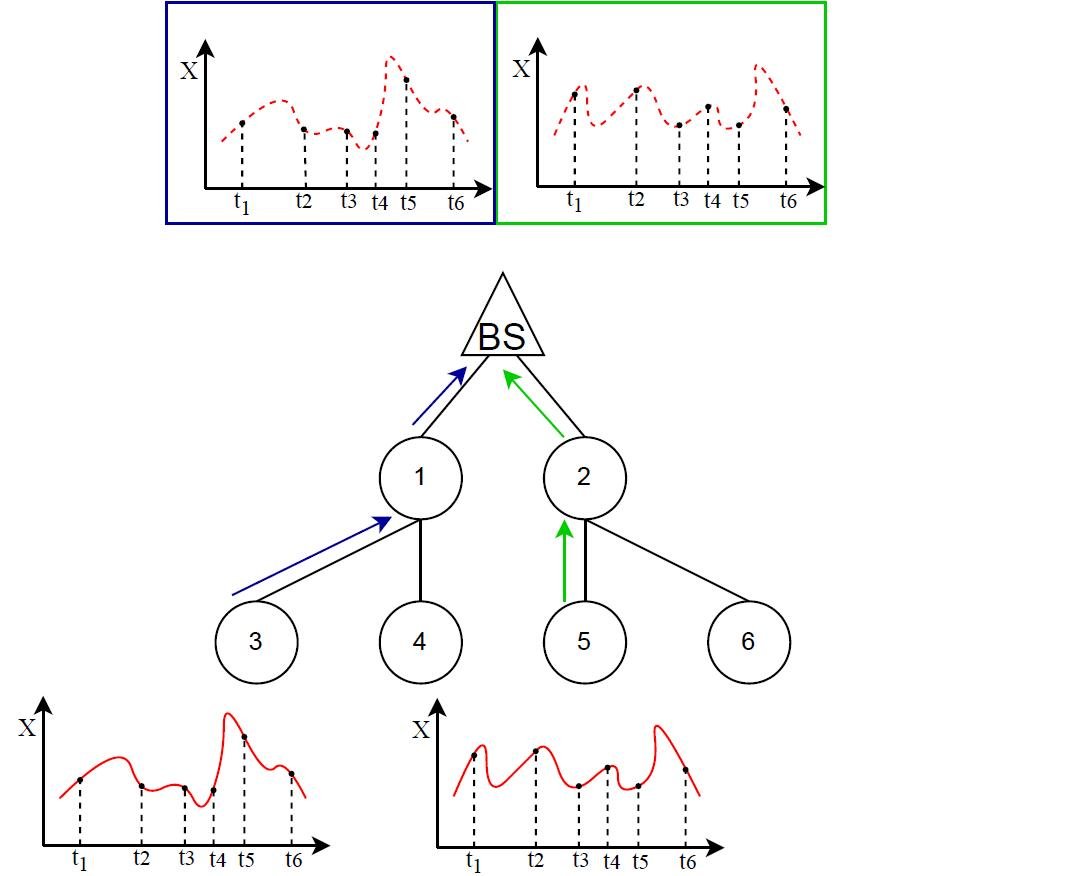
This project focuses on multihop wireless networked control systems (WNCS) for industrial applications, particularly in smart factories. In such systems, robots and other entities operate using a sense-compute-actuate cycle, where control algorithms are executed remotely over a wireless network. For example, a mobile robot may sense an object using video, transmit data via a multihop wireless network, receive control commands from a remote server, and act accordingly. To ensure efficient operation, the freshness of information is critical, measured using metrics like Age of Information (AoI) and Age of Incorrect Information (AoII). This project aims to design scheduling policies for IEEE 802.15.4e Time-Slotted Channel Hopping (TSCH) networks that minimize AoI, optimizing performance for remote estimation and control applications in industrial IoT environments. For instance, in a remote estimation scenario (Figure 1), sensor nodes (e.g., sensors 3 and 5) monitor processes of interest and generate data packets containing real-time observations. These packets are transmitted over a multihop network to a destination node that computes remote estimates for monitoring or control. AoI has been widely used to quantify information freshness, alongside other metrics such as AoII and the Value of Information (VoI). This project focuses on designing efficient multihop sampling and scheduling policies to minimize these freshness metrics, thereby enhancing the reliability of industrial IoT networks
